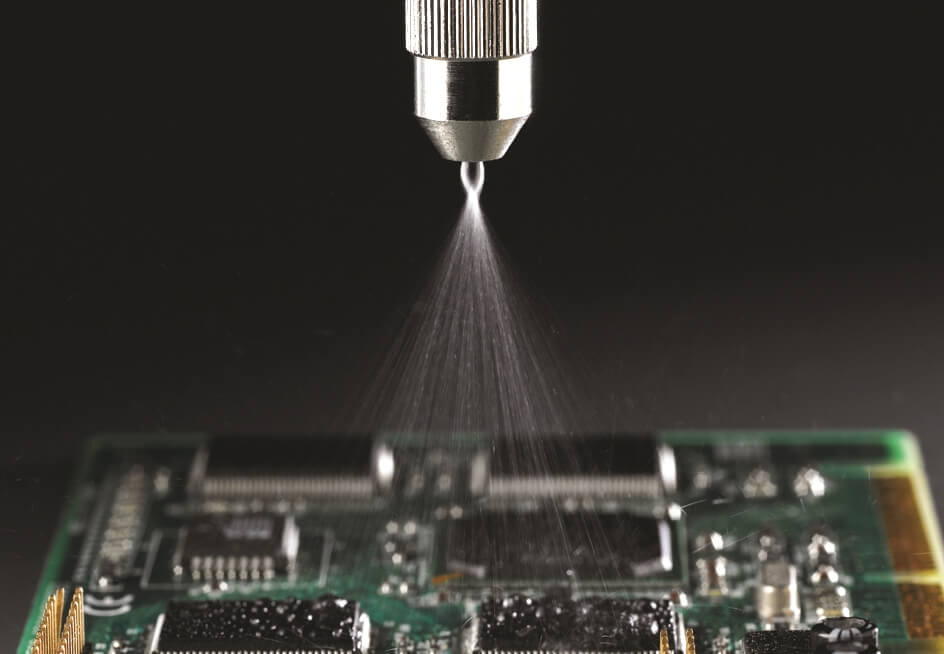

What is Conformal Coating and Why is it Used?
Conformal coating is a thin polymer layer applied directly to printed circuit boards (PCBs). Thanks to its ability to conform precisely to the shape of the board, it provides excellent protection against harsh environmental conditions. It is particularly preferred in applications requiring electrical insulation, corrosion prevention, and mechanical durability. Its key advantages include:
- Comprehensive Protection: Shields the circuit board from moisture, salt spray, and chemical exposure.
- Electrical Insulation: Prevents unintended currents from spreading across the circuit surface.
- Durability: Extends the lifespan of the circuit board even under harsh operating conditions.
Essential Features of a High-Quality Conformal Coating Application
A high-quality surface protective coating should focus on reliability and performance. The key characteristics of an ideal coating include:
- Dielectric Strength: Minimizes the risk of electrical discharge.
- Flexibility: Resistant to temperature changes, reducing the risk of cracking.
- Excellent Adhesion: Provides long-lasting protection on all PCB surfaces.
- UV Traceability: Facilitates quality control and inspection.
- Moisture and Salt Spray Barrier: Prevents corrosion of the circuit board.
- UV and Chemical Resistance: Ensures effective protection even in harsh environments.
- Resistance to Solvents and Corrosive Gases: Enables long-term use in industrial settings.
Types of Conformal Coating
Various types of conformal coatings are available to meet different application needs:
- Silicone-Based Coatings: Provide superior performance in high-temperature environments.
- Acrylic Coatings: Offer effective protection against factors such as salt spray and moisture.
- Polyurethane Coatings: Resistant to chemicals while maintaining flexibility.
- Hybrid Coatings: Combine the best properties of multiple materials to provide customized solutions.
Conformal Coating Application Methods
The choice of application method depends on the specific requirements and characteristics of the coating material. The most common application methods include:
- Spraying or Dipping: Ensures an even coating layer on the surface of the board.
- Selective Application: Used when only specific areas need to be coated.
- Manual Application (Brushing): Preferred for small areas or touch-up processes.
Each method has its own advantages and disadvantages, all aimed at ensuring safe and efficient PCB protection.
